Acid reflux Center
Acid reflux or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a condition whereby stomach acid flows back to the food tract (esophagus). This irritates the lining of the esophagus. There are mild cases of GERD that people can easily cope with using over the counter medication and a change of lifestyle. However, there are severe cases that may require surgery or stronger medications.
Read: What is Acid Reflux?
Acid Reflux Center
Common symptoms of acid reflux include:
- Heartburns or burning sensation after eating
- Chest pains
- Feeling of a lump in the throat
- Difficulty in swallowing
- Regurgitation of sour liquid or food
- Laryngitis
- Chronic cough
- Disrupted sleep
Read: Acid Reflux Symptoms
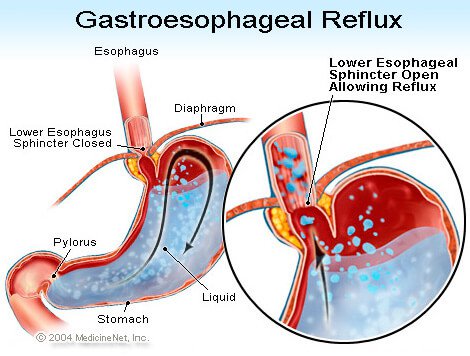
When food is swallowed, the lower esophageal sphincter (circular muscles at the bottom of the esophagus) relaxes to allow food and liquids to enter into the stomach. Once the swallowing is through, the sphincter closes. The stomach acid therefore flows back to the food duct because the sphincter is weak or it relaxes abnormally. Constant acid refluxes irritate the esophagus and may lead to its inflammation.
Factors that increase acid reflux include:
- Obesity
- Pregnancy
- Bulging at the top of the stomach up to the diaphragm
- Connective tissue disorders
Factors that aggravate GERD include:
- Eating large meals
- Eating late at night
- Fatty and fried foods
- Smoking
- Beverages, such as coffee and alcohol
- Certain medications, e.g. aspirin is a good trigger of GERD
- Delayed bowel emptying
Chronic inflammation in the esophagus can lead to:
- Esophageal stricture. Stomach acid damages the lower part of esophagus leading to formation of scar tissue. The scar tissue narrows the esophagus, leading to swallowing problems.
- Esophageal ulcer. The stomach acid wears out esophageal walls forming open sores. These ulcers cause a lot of pain, bleed and make swallowing hard.
- Risk of esophageal cancer. Damaged tissues in the lower esophagus may change from their natural form. These changes may lead to esophageal cancer
Causes:
Read: Acid Reflux Causes
Diagnosis:
Read: Acid Reflux Test
Treatment:
Read: Acid Reflux Treatment

