FODMAPS is the acronym for Fermentable Oligo-, Di- and Mono-saccharides, and Polyols (1).
They are a group of fermentable carbohydrates that lead to digestive distress in the form of bloating, diarrhea, and they are the link to irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) (2), (7), (8), (9).
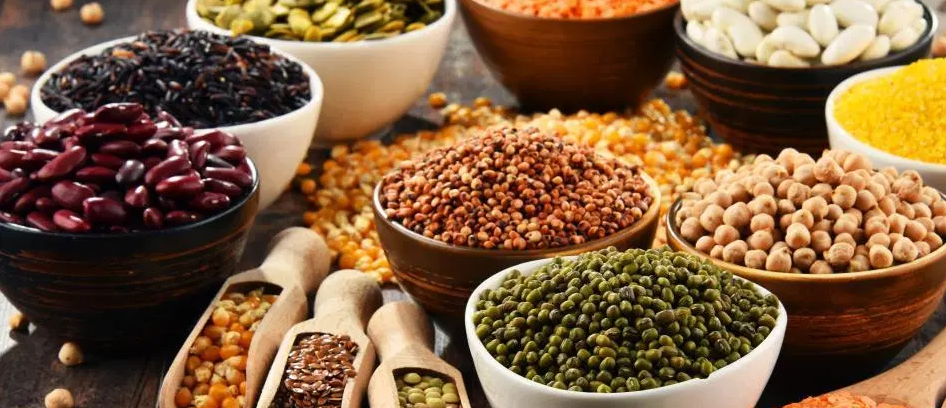
There are many types of FODMAPS, and they are in several types of food groups. There are four main groups of FODMAPS. They include Oligosaccharides, Disaccharides, Monosaccharides, and Polyols. Foods with FODMAPS can irritate the gut microbiome, especially for those with underlying digestive issues such as IBS (8),(9).
Tip: Work with a Registered Dietitian if you think a low FODMAP diet is the right direction for you. Following a low FODMAP diet is very individualized, and can cause more complications if done without expert help.
Table of Contents
Foods low in FODMAPS
A low FODMAP diet can be necessary for those with digestive issues, and it can also be helpful for those who may be sensitive to these fermentable carbohydrates, even if they don’t know it (9), (10). See what foods are low in FODMAPS if you suffer from digestive distress associated with a digestive disorder like IBS. Try to incorporate these into your diet more to learn what works best for your body.
Many foods are naturally low in FODMAPS (3). Below, we’ll go into some of the common staple foods for a traditional low FODMAP diet. Check out the list of low FODMAP foods below to see what might work well for you and your individual needs.
Tip: Because the low FODMAP diet eliminates many foods, it’s important to load up on nutrient-dense low FODMAP foods to ensure nutrient deficiencies do not occur.
1. Protein
The most common staple food across the globe is a part of the low FODMAP diet, protein (11). Protein like chicken, eggs, pork, tofu, lamb, and beef are all good choices if you want to follow a low FODMAP diet (11). Make sure to always buy the lean versions of the meat protein for the most health benefits. Pork can be extremely fatty, so be sure you are choosing the best options for you.
Chicken, lamb, and beef are the leanest meats to consume (13). Eggs are a great source of protein with plenty of added nutrition like vitamin D, A, lutein, and more. Mix in some tofu to your diet if you want a break from the meat. Tofu makes an excellent nutritional source of plant-based protein to replace eggs and meat on occasion (12), (13). If you can eat all of these proteins in your diet, mix them up as much as you can to get the varying nutritional benefits.
Tip: Low FODMAP proteins include chicken, beef, pork, lamb, tofu, and eggs. For vegetarian or vegan diets, many beans are high in FODMAP, so it’s important to incorporate tofu or eggs to meet protein needs.
2. Seeds
The most common types of low FODMAP seeds include pumpkin, sesame, sunflower seeds, and linseeds (4), (14). Seeds, especially linseeds, are high in fiber so they are powerful for the reduction of constipation (15).
Seeds are easy to add to most diets. Add them to your smoothies, oatmeal, yogurts, and many more of your favorite meals. Or just snack on them plain for the many health benefits.
Tip: Pumpkin, sesame, sunflower, and linseeds are all low FODMAP seeds. Add them into your daily routine to boost fiber and nutrient intake.
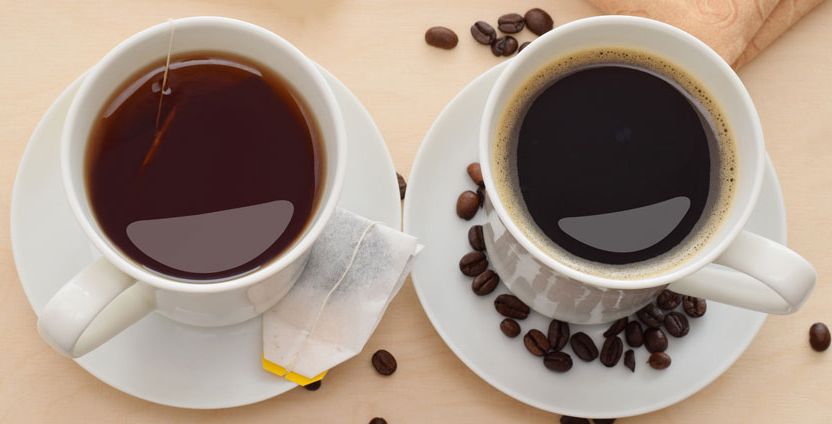
3. Tea
Tea is an extremely healthy option to include in most diets, and that goes for low FODMAP diets, too. There are a few teas low in FODMAPS, including peppermint tea and green tea.
Peppermint oil and tea can be effective at reducing the symptoms of IBS (5), (16). Green tea is a natural anti-inflammatory with many helpful compounds that can also benefit IBS and other digestive distress (17). Avoid fennel, chamomile, and black teas like oolong tea, as they are high in FODMAPS.
Tip: Peppermint tea and oil is a low FODMAP option that may improve IBS symptoms. Avoid high FODMAP fennel, chamomile, black, and oolong teas.
4. Some Condiments and Spices
Many condiments and spices are a great addition to a traditional low FODMAP diet. One is the powerful spice turmeric, particularly in the form of curcumin (6). Curcumin is the most anti-inflammatory compound in turmeric and it’s widely in supplements to reduce symptoms of inflammatory conditions, such as IBS (18), (19).
Other condiments and spices that can be helpful when following a low FODMAP diet include mustard seed, basil, coriander, thyme, parsley, rosemary, basil, garlic, chives, and more. This diet low in FODMAPS doesn’t have to lack flavor. It can be plenty flavorful with all of these ingredients and more (2). Another ingredient you can add to most meals for a ton of flavor is spring onions, but only the green part.
Tip: Turmeric is a low FODMAP spice that helps reduce inflammation and improve IBS. Incorporate other low FODMAP spices like mustard seed, basil, coriander, thyme, or parsley daily.
5. Whole Grains
Whole grains are an easy addition to a low FODMAP diet, too. Enjoy whole grains like oat, brown rice, buckwheat, quinoa, and millet. Whole grains contain insoluble fiber, which is necessary for this type of diet. Try to skip out on the white bread alternatives if you can. Refined carbohydrates can exacerbate IBS symptoms (2).
Switch up your typical white rice for brown rice or quinoa for a hearty and nutritious change. Enjoy oats and buckwheat for breakfast instead of sugary granola alternatives. Adding this food group to your diet can be easy and tasty. Plus, it will benefit the health of your gut microbiome tremendously (20), (29).
Tip: Oats, brown rice, buckwheat, quinoa, and millet are fiber-rich and high in B vitamins. Swap regular white alternatives with these whole grain options to boost nutrient intake.
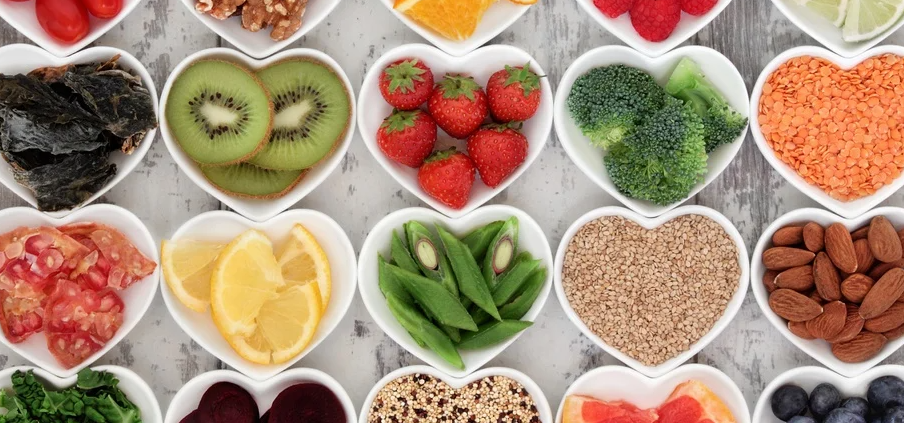
6. Certain Fruits and Vegetables
Some fruits and vegetables are naturally low in FODMAPS, making most of them an excellent nutritious option for this diet. These include vegetables high in insoluble fiber like green peas, carrots, spinach, sweet potatoes, and much more (21), (2).
Fruits are high in soluble fiber, which can improve the symptoms of digestive distress like IBS. But be careful about which you choose. Try to eat more fruits like blueberries, bananas, oranges, pineapple, papaya, avocado, grapes, olives, and more (22).
Tip: Low FODMAP fruits and vegetables include green peas, carrots, spinach, sweet potatoes, avocado, grapes, olives, blueberries, bananas, oranges, pineapple, and papaya. Consult with your Registered Dietitian for a complete list.
7. Coffee
Coffee can be healthy for some individuals (25). Coffee and the caffeine in it act as a natural laxative and can be helpful for those with IBS (26). Everyone is different in how they react to certain foods, however (23).
While coffee has its health benefits, some can be sensitive to the high amount of caffeine. It can affect hormone levels, and much more (24). Some tolerate coffee quite well, while others get side effects like enlarged pupils and shaking hands, for example (26), (30). Be sure to ask your doctor if you think something isn’t working for you on your low FODMAP diet.
Tip: Coffee is low in FODMAPs, but the caffeine may exacerbate IBS symptoms. If it causes issues for you, swap it with green or peppermint tea.
8. Dairy
The best type of dairy to include in a low FODMAP diet is lactose-free milk and yogurt, and certain cheeses like cheddar, parmesan, and other hard cheese. Dairy is high in a plethora of vitamins and minerals like vitamin D, A, and calcium, and it can be an effective option to help those with IBS (2).
However, dairy is also an extremely sensitive food group for many. While you may be ok with lactose-free milk, certain cheese may bother you, for example. Simply because something is considered low-FODMAP, doesn’t mean it’s going to have the same effect for everyone. If you are lactose-intolerant or just sensitive to dairy, leave this option out. You can replace your vitamin D, A, and calcium with green vegetables, eggs, and more (27).
Tip: Lactose-free milk and yogurt, and hard cheeses like cheddar and parmesan are great low FODMAP options rich in vitamins A, D, and calcium.
9. Nuts
Choose nuts in moderation like peanuts, pecans, pine nuts, and walnuts (2). These are the easiest on the digestive system but also high in fiber and nutrients. It’s important to keep your nut consumption to a minimum because too much fat (mostly found in walnuts and peanuts) can cause too much distress on the digestive tract (26). But incorporating small amounts can be helpful.
Add some healthy nuts to your favorite meals in place of unhealthy ingredients. Instead of sugar-laden granola, add in a few walnuts to your yogurt or oatmeal. Pine nuts are an excellent nut to lightly toast on the stove and add to many vegetable dishes. They go great with starchy vegetables like sweet potatoes and even a vegetable as simple as spinach.
Tip: Small amounts, about 1/4 cup or a small handful, of peanuts, pecans, pine nuts, and walnuts are perfect for meeting healthy fat and fiber intake when on a low FODMAP diet.
10. Coconut and Olive Oil
It’s time to cook some of these delicious foods, so what should you cook with? Choose coconut or olive oil. Coconut oil is best when cooking foods at high heat temperatures. Use olive oil when you are cooking at lower heat temperatures 375 degrees or lower (28).
At high temperatures, olive oil can create free radicals, defeating the healthy purposes of using it in the first place (28). Olive oil also works great as a salad dressing with lemon and maple syrup. Get creative in the kitchen and see where you can add these beneficial omega 3-rich essential fatty acids to your diet more often. There is no need to overdo it, a teaspoon or tablespoon a day usually does the trick.
Tip: Coconut or olive oils are low FODMAP-friendly cooking oils. It’s best to cook olive oil at lower temperatures, like light sautéing or baking 375 degrees or less, because they omit free radicals when cooked at high temperatures.
Conclusion
FODMAPS are in many different foods like the ones above and much more. Although there is a variety of FODMAPS, there are four main FODMAP types, and each food group varies. Some have one, while others have all.
Start to monitor your daily diet more if you suffer from digestive issues such as IBS. See if any of these foods can make a difference for you. Simplify your diet by sticking to whole foods like these and more. Make sure you pay close attention to what foods trigger digestive distress symptoms for you. Personalize the list above to what your body needs.