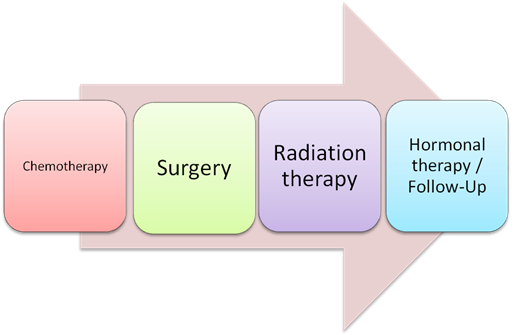
Leukemia treatment is a highly complex decision and action to be taken. Surely, the treatment for leukemia varies according to the type and the patient, so a doctor must plan a treatment that fits the needs of the individual. There are many things to be taken into consideration when creating the plan for treating Leukemia such as the leukemia cells’ features, the progress of the disease, the extent of the disease, and the previous medical history of the patient. Additionally, this also depends on the age of the patient, symptoms, and general health.


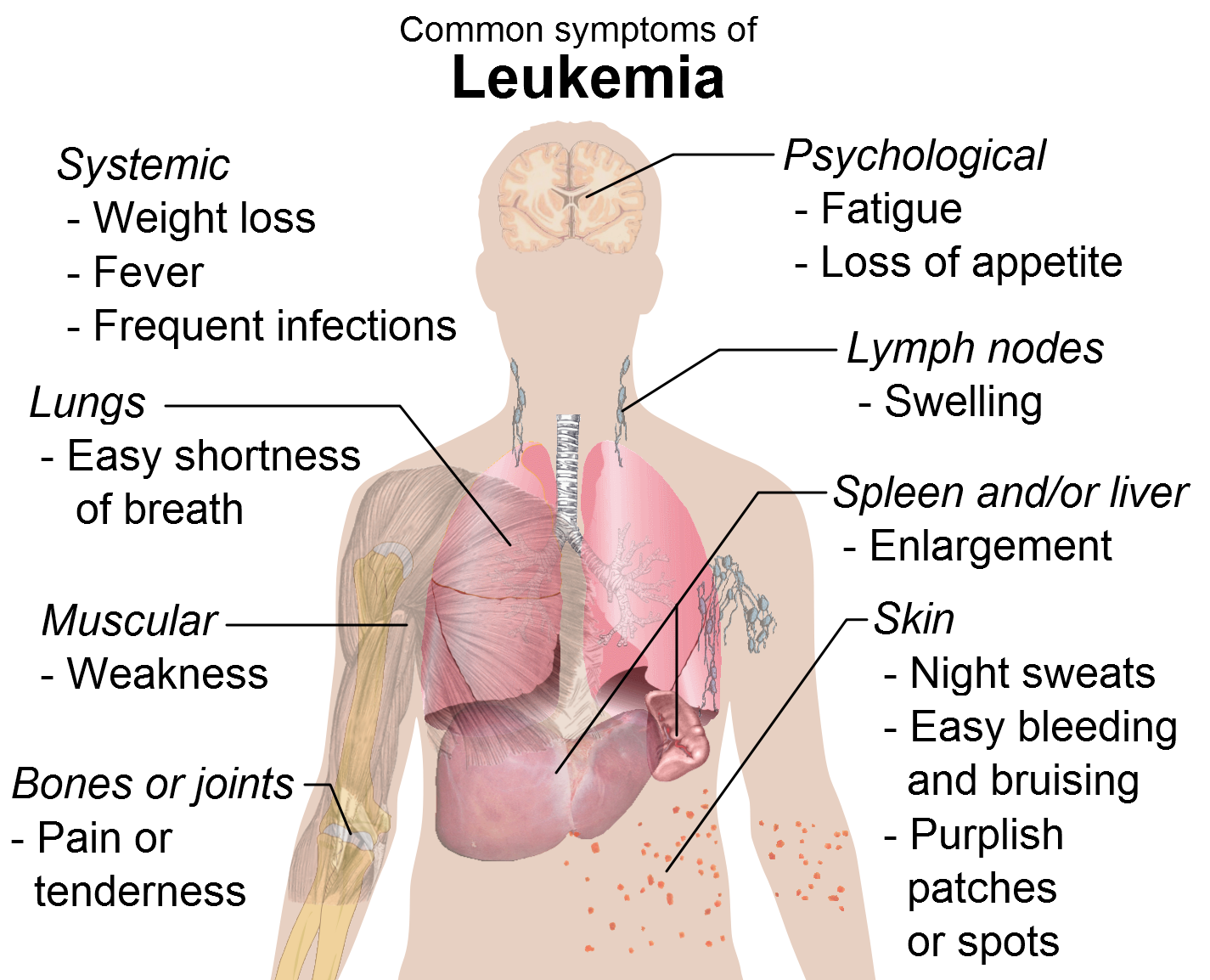
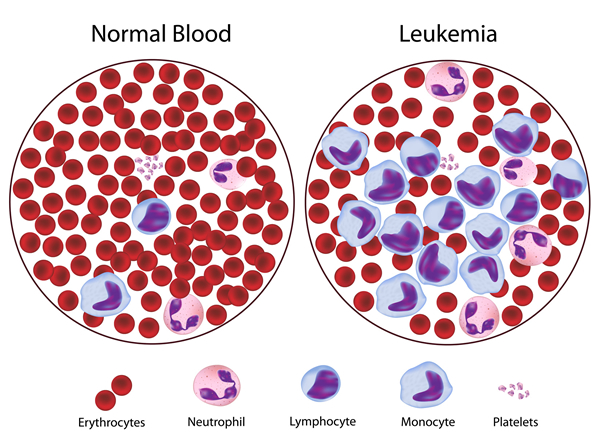
There are many signs and symptoms associated with this disease and they all depend on the leukemia type. The most common ones are fever, fatigue, frequent infections, loss of weight, enlarged liver or spleen, swollen lymph nodes, easy bruising, excessive sweating, recurrent nosebleeds, etc.
Leukemia Treatment
Patients, who suffer from this condition, should be treated at a hospital when possible so that the experts that have knowledge of the treatments can overlook the progress of the disease and the progress of the treatment. If this is not an option, the doctor should be the one to plan and discuss the treatment for leukemia with the patient who is diagnosed with it and schedule regular visits to see if this particular treatment is effective or not.
There are different types of leukemia. When it comes to acute leukemia, the need to be treated is immediate. The goal of the treatments for acute leukemia is to bring about remission. When the disease has no evidence of being present, some additional therapy may be recommended in order to avoid recurrence. Even though there is no specific leukemia cure, many patients who suffer from acute leukemia can be cured.
On the other hand, chronic leukemia patients without any severe symptoms may not require immediate action but are highly recommended to have frequent checkups in order to be aware of the progress of the disease. Unfortunately, this is a type of leukemia that can rarely be cured. The treatment for chronic leukemia can help control the symptoms and the disease.
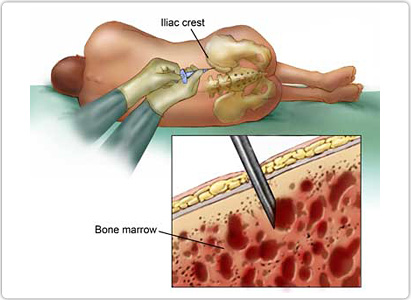
The majority of patients that suffer from leukemia are treated with chemotherapy. Some may have bone marrow transplantation, radiation therapy, or even spleen removal surgery. This depends on the treatment plan that is based on the type of leukemia, the progress of leukemia, and the health of the patient.
Treatment for Acute Leukemia
1. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia treatment
The majority of the plans for treating acute lymphoblastic leukemia consist of 3 steps: induction, consolidation, and maintenance.
- The first therapy kills the leukemia cells that are located in the bone marrow and the blood. This is done with the purpose of inducing remission. Such treatments include chemotherapy and corticosteroids and the induction treatment usually lasts up until 4 weeks and is done in hospitals. In cases where patients have cells of leukemia with a certain gene change called the Philadelphia chromosome, the treatment includes a tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
- The consolidation therapy kills cells that may or may not be present in the tests. The reason behind this is that the regrowth of these can cause a relapse. These treatments include chemotherapy done more often and may even include stem cell transplants. Additionally, consolidation therapy may include preventive treatment of the spinal cord or the brain with radiation. This process takes up to several months, but the patient does not need to be hospitalized.
- The last step is maintenance therapy. This step prevents any remaining leukemia cells from further growing and can be done by using lower chemotherapy doses than those used in the previous steps. The chemotherapy is given orally, with pills and monthly intravenous treatment. This treatment lasts up to 3 years, but people can live a normal life while in this phase.
A person is considered cured when there is no leukemia sign for 5 years. However, if existing leukemia does not go into remission or comes back within the first few years, more chemotherapy or some other treatment may be recommended.
2. Acute myelogenous leukemia treatment
This leukemia treatment can be based on fixing the abnormal myeloid cells. This plan usually consists of 2 steps: induction of remission and post-remission therapy.
- The first one kills the leukemia cells in the bone marrow and the blood in order to induce remission. The chemotherapy is given by an IV treatment and the period usually lasts for 4 weeks. The first week is chemotherapy week while the rest are weeks for recovery of the bone marrow. The patient is hospitalized during this treatment.
- Post–remission therapy is the process where remaining leukemia cells are killed, even if they cannot be noticed in the test results. This may involve another chemotherapy treatment or a stem cell transplant. Also, the doctor may recommend a certain clinical trial for the introduction to new treatments.
If you are suffering from a subtype of acute myelogenous leukemia, also referred to as acute promyelocytic leukemia, you may be recommended to take medicines such as arsenic trioxide or all-trans retinoic acid. Additionally, chemotherapy and stem cell transplants are also recommended when this leukemia type does not respond to the mentioned treatment or if it comes back after a while.
Treatment of chronic leukemia
1. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia treatment
There are several treatment choices for CLL, such as:
- Radiation therapy (commonly used for treating swollen lymph nodes)
- Chemotherapy (may include monoclonal antibodies)
When this type of leukemia does not respond to the treatment or returns after being cured, another chemotherapy or stem cell transplant may follow. Additionally, the doctor may recommend joining clinical trials for new leukemia treatment.
Having chronic lymphocytic leukemia makes your body unable to fight infections, so you must watch carefully for any signs of infections such as yeast infections or pneumonia. You will live longer if you notice the signs early and are treated right away. Sometimes, a flu shot or a pneumonia vaccine is a good way to keep you healthier.
2. Chronic myelogenous leukemia
This type of leukemia must be treated right away. The treatments include:
- Tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeted therapy
- Stem cell transplant preceded by chemotherapy or radiation.
People who are diagnosed with CML in the beginning stages of the disease can be maintained in good health by the tyrosine kinase inhibitors for years before the disease worsens. If they do not have a relapse, they do not need a stem cell transplant. However, in cases when they do, they will need this treatment of leukemia.
Clinical Trials
Doctors will often recommend clinical trials as the most prospective option for the survival of patients suffering from an incurable or highly progressed leukemia. These trials are used to constantly test new treatments and drugs that have often helped people live longer. People included in such trials are closely watched.
Leukemia Treatment in Children
Leukemia can occur in all ages, but treatment for children is not the same as that for adults. Children are monitored after the treatment for side effects that can appear at any time later in life.
Treating childhood ALL
ALL is the most common leukemia in children and the treatment for adults does not apply in these cases. There are different treatments for children, infants, and adolescents. These include chemotherapy, radiation; chemotherapy combined with stem cell transplant, and targeted therapy.
The treatments of children have improved and increased survival rates.
Treating childhood AML
This disease in children can be grouped with other myeloid diseases that affect both the bone marrow and the blood. The treatment varies depending on the type but will include chemotherapy, radiation, stem cell transplant, or targeted therapy.
Palliative and end-of-life care
These are introduced to help patients cope with their disease. The first one is one that prepares the patient, helps him understand and make his own choices. The second one is used for people with advanced leukemia that do not have a chance of survival or improvement with any available treatment. However, it is up to the patient whether he would want to continue getting leukemia treatments.
Natural Treatment for Leukemia
There are things to be done at home in order to manage leukemia’s side effects. Healthy habits that include a balanced diet, regular exercise, and enough sleep may help greatly in controlling the symptoms.
- If the patient is vomiting or feeling nauseous, this treatment should include watching closely for signs of dehydration. Smaller portions of meals and ginger may help in this case.
- If the patient is experiencing diarrhea, treatment includes resting the stomach and watching for dehydration signs.
- Treatment for constipation includes exercising and drinking fluids. Additionally, the patient must eat a diet high in fruits, fiber, or vegetables.
- Sleeping problems can be treated by exercising and going to bed at a particular, regular time of the day.
- If the patient lacks energy, more rest may help
- Hair loss can be treated using a soft hairbrush and a mild shampoo
Other Leukemia Treatments
1. Chemotherapy
This is the standard treatment, used for the majority of leukemia types. This treatment can actually help people with no chance of survival live longer.
Chemotherapy is a treatment that uses a drug combination. A combination of certain drugs can attack leukemia cells and keep them from being resistant to other drugs that are used in the treating process.
Other medicines may also be given in addition to chemotherapy and these are most commonly prescribed in order to help the drugs used in chemotherapy in working better and prevent bleeding or infection. These include hematopoietic stimulants and epoetin.
Regular chemotherapy cannot reach the brain and the spinal cord, so in cases of acute leukemia that spread to these areas, this treatment will not help. There is another way of giving chemotherapy that is used in these cases and this is called intrathecal chemotherapy. This is done by injecting drugs into the spinal canal.
2. Medication
Acute Leukemia Medicines
The treatment plan includes the best medicine available for the type of leukemia of the patient.
- ALL can be treated with chemotherapy medicines that include daunorubicin, clofarabine, asparaginase, doxorubicin, nelarabine, vincristine, and methotrexate. Additionally, corticosteroids such as dexamethasone or prednisone may be recommended.
- AML can be treated with cytarabine, idarubicin, daunorubicin, and mitoxantrone, all chemotherapy medicines.
- APL can be treated with chemotherapy medicines that include daunorubicin and idarubicin. Also, arsenic trioxide and all-trans-retinoic acid may be recommended.
Chronic Leukemia Medicines
- CLL can be treated with chemotherapy medicines that include chlorambucil, bendamustine, cyclophosphamide, fludarabine, or vincristine. Additionally, it may be treated with prednisone (a corticosteroid) and monoclonal antibodies such as rituximab or alemtuzumab.
- CML patients that are not allowed to have stem cell transplants and are also not able to take tyrosine kinase inhibitors are normally given hydroxyurea, busulfan, and interferon alfa.
The medicines that are used to treat CLL are given either orally or intravenously, for a limited period of time. For CML, the medicine is given orally for as long as the patient needs it.
Medicine for vomiting and nausea
These two are very common chemotherapy side effects that usually occur after the end of the treatment. There are many medicines that doctors can prescribe to help relieve nausea.
3. Surgery
There are rare cases of CLL where the spleen needs to be removed from the body. This happens when this organ destroys the blood cells and the platelets and the surgery is also referred to as splenectomy.
Another leukemia surgery is lymphadenectomy. This surgery is done to remove a lymph node in order to confirm leukemia.
Surgery is also needed in order to place a venous catheter into a chest large vein. This tube is used to give chemotherapy.
Living and fighting leukemia is not an easy task and should be taken seriously. The need for professional help is always present in the lives of people who suffer or have suffered from this disease.