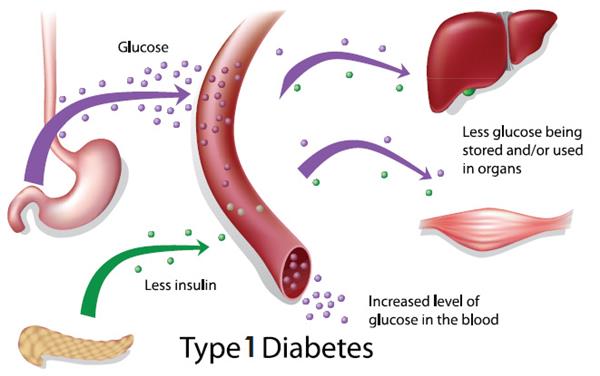
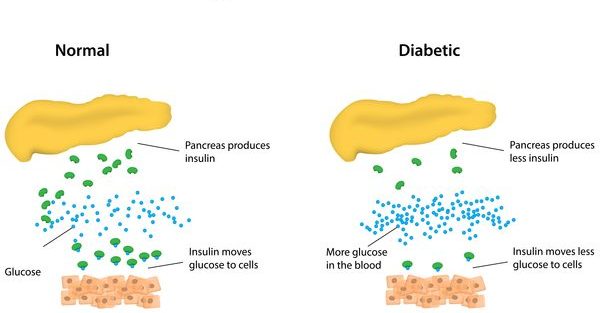
Type 1 Diabetes or otherwise referred to as juvenile diabetes is a chronic condition. This condition is present with patients whose pancreas has reduced insulin production or produces no insulin at all. Insulin is a hormone needed in the process of allowing glucose to enter the cells. This is a crucial element in the producing process of energy in the body. Unfortunately, despite all active research, there is no defined type 1 diabetes cure present so far. However, proper type 1 diabetes treatment can be managed properly and with the utmost care and people suffering from this condition can expect to live a long and happy life.



Table of Contents
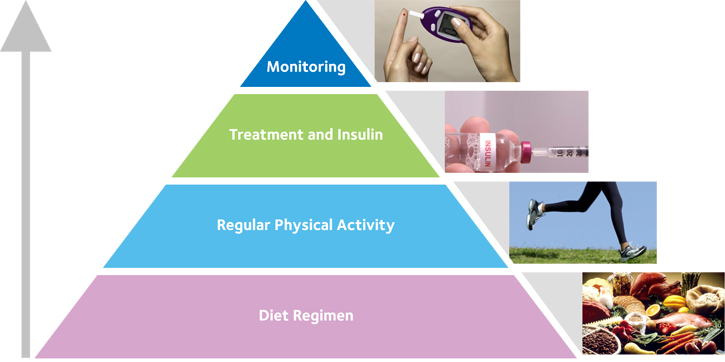
Type 1 Diabetes Treatment
Generally speaking, there are various factors that may contribute to the existence of this condition, including virus exposure and genetics. This particular type of diabetes most often occurs during childhood or adolescence, but can also begin in adulthood.
The importance of insulin
When the islet cells are being partially or completely destroyed, the pancreas produces less or no insulin. Insulin is the hormone produced in the pancreas, an organ located behind and below the human stomach. The main purpose of this organ is to secrete insulin into the bloodstream, circulate and enable sugar to enter the blood cells. This hormone has the task of lowering the sugar amount in the bloodstream. As this process happens, the secretion of insulin also adjusts and production drops accordingly.
The importance of sugar – glucose
The glucose is the main energy source the cells need to make up tissues and muscles. We provide our body with glucose by consuming food and with the help of the liver. The liver is known to be the second major source for glucose production that additionally stores glucose as glycogen. Sugar is absorbed into the bloodstream and enters the cells with the help of the insulin. The insulin then controls the levels of glucose. Additionally, when glucose levels are low, the liver converts glycogen into glucose and keeps the levels in the normal range.
When it comes to type 1 diabetes, the problem is that no insulin transfers glucose to the cells and no sugar build up the bloodstream. Additionally, there is no such thing as insulin production control because the main function of the pancreas is partially or completely destroyed.
Type 1 diabetes risk factors
There are several known risk factors when it comes to a diabetes of this type:
- Family history. If you have a parent or a sibling diagnosed with diabetes, you have a slightly increased risk of developing this condition
- There are certain genes in the body that indicate increased risk of developing type 1 diabetes
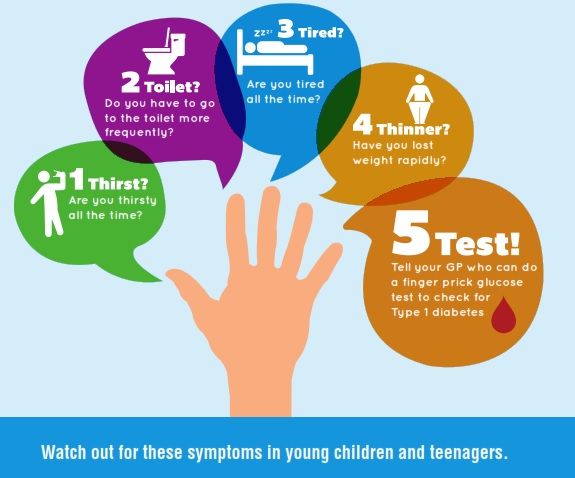
- Type 1 diabetes most often appears in children between 4-7 years old and children between 10-14 years old. However, it can still appear at any age.
- The chances of getting this condition increase as you travel away from the equator. For example, people who live in Sardinia and Finland are most exposed to the incidence of type 1 diabetes. The percentage here reaches about three times higher rate than those in the US and 400 times than those in Venezuela
- Exposure to certain viruses
- Early exposure to cow’s milk
- Low levels of vitamin D
- An early or late introduction of gluten into a baby’s diet
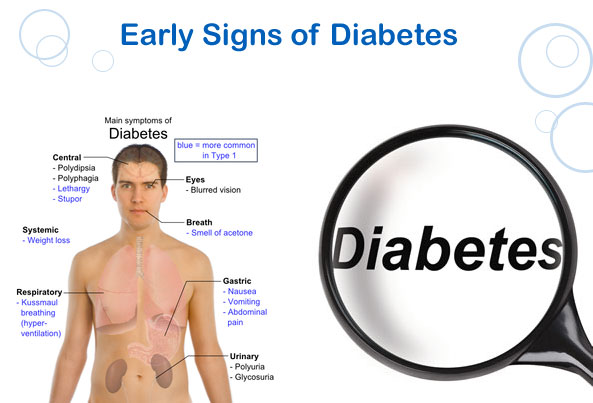
Complications of type 1 diabetes
This type can affect many of the major body organs among which are the heart, nerves, blood vessels, eyes, and even the kidneys. Maintaining a normal sugar level for the majority of time will reduce the risk of complications.
When speaking of long-term complications, these tend to develop gradually and can be avoided by good blood sugar management. The risk of these complications is not only bad to overall health but may also turn up to be life-threatening and disabling.
Is there a cure for Type 1 Diabetes?
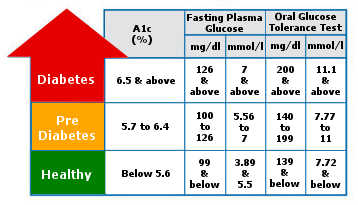
As previously mentioned, no, there is no known cure for diabetes. However, it can be kept under control. Once you’ve been diagnosed with this condition, you have to make regular visits to your doctor’s office to maintain your health and manage diabetes. The doctor’s job here is not only to advise you, but also to check your A1C levels. The expected results vary depending on many factors such as age, but the American Diabetes Association has recommended that these levels should be considered normal if they are below 7 percent.
This test actually indicates how well you are maintaining your diabetes treatment and whether the type 1 diabetes treatment needs to be somewhat modified or completely replaced by a new one. An elevated A1C level indicates a need for change in meal plan or insulin regimen, sometimes even both.
In addition to this regular testing, both your blood and urine will be examined periodically to check the condition of your cholesterol, thyroid, kidney, and liver.
Lifestyle with type 1 diabetes
Diabetes should be treated with the utmost care, which sometimes can be frustrating. However, medicine has now helped patients live a long life with diabetes, so this is worthwhile. When it comes to diabetes lifestyle, you should:
- Make a commitment
If you are suffering from this condition, it is a serious thing. This is why you must make a commitment to manage your diabetes and learn all you can about it. Try to engage in physical activities daily and eat healthy food.
- Identify yourself to others
You are now a constant patient, so you should always identify yourself as a diabetic. You could wear a tag or a bracelet that says you are a diabetic or even get a tattoo on your arm that will stick there forever. Always wear a glucagon kit and some sweets with you and make sure your friends and loved ones know how to use it and help you.
- Schedule regular visits at the doctor’s office
You have to schedule regular diabetes checkups, where the doctor will check your current condition and make sure there are no complications related to diabetes.
- Schedule regular eye exams
An eye care specialist should regularly check your eyes for signs of cataracts, glaucoma or retinal damage.
- Keep immunization up to date
You are having a condition that weakens the immune system, so make the habit of getting a yearly flu shot. Additionally, you may be recommended to take the pneumonia vaccine as well.
- Keep your cholesterol and blood pressure under control
This can be done through regular exercise and healthy nutrition. You may even need some medications if you are having trouble with blood pressure and cholesterol.
- Regularly check your feet
As a diabetic, you should start the habit of washing your feet in lukewarm water daily. Dry them gently, moisturize them and check for sores, cuts, blister, swelling or redness. If you notice anything strange, consult your doctor.
- Quit smoking
Smoking is bad for everyone, but it is especially bad for people suffering from diabetes. It increases the risk of complications such as nerve damage, kidney disease, and heart attack. If you have this condition and smoke, you are three times more likely to die prematurely than people who don’t have it.
- Do not stress
Stress can also cause complication and prolonged stress may prevent insulin from working properly.
Type 1 diabetes treatment options
1. Insulin
Anyone diagnosed with diabetes of type 1 needs insulin therapy at some point. There are a few types of insulin:
- Long-acting
- Rapid-acting
- Intermediate
This therapy cannot be taken orally because the enzymes in the stomach interfere with the insulin. Therefore, the only 2 ways to administrate insulin is through injection or a pump. Injections include fine needle and syringe or an insulin pen. A pump is a device with the size of an average cell phone and is worn outside the body. There is a tube that connects the reservoir filled with insulin to a catheter inserted under the skin. There are many ways to wear the pump: on the waistband, in the pocket or with designed pump belts. Additionally, there is a wireless pump option now, where you wear a pod on your abdomen, lower back or an arm and use a wireless device to control it.
Pumps are normally programmed to dispense an automatic amount of insulin, known as a basal rate.
2. Artificial pancreas
This is an emerging treatment and is not available right now but will presumably be in the near future. This is an artificial pancreas that links a glucose monitor to a pump with insulin. It automatically delivers the needed amount of insulin when the monitor indicates the need of it.
3. Additional diabetes medications
These include:
- An injection of pramlintide prior to eating
- High blood pressure medications
- Aspirin
- Cholesterol medications
Support for type 1 diabetes patients
This is a condition that can be managed but can often be frustrating and difficult to handle. Diabetes can take a lot of time and effort and affect emotions directly and indirectly. Your emotions will especially be affected if blood sugar is not properly controlled. Additionally, this condition often makes people feel different than others because of the specific way of life they must be living. There may even be depression periods when you are resentful about having to live with this disease.
Diabetes-related distress and depression are common with diabetics and people with this condition are at an increased risk of feeling bad about themselves. This is why many specialists in the field include a psychologist or a social worker in the care team of diabetics.
If you are having trouble coping with this disease, perhaps you should try to talk about it with people who suffer from the same condition. Luckily, there are many support groups to be found and they will be more than happy to share their experiences with you. Additionally, you could learn a lot and see them as a good source of important information. Group members often know about clinical trials, latest treatment and share this information with others, so you may really benefit from it.
Although there is no cure for diabetes type 1, one must not feel frustrated. This is one of the rare diseases that can be controlled to such levels and with such ease that the person can live their entire lives normally without it affecting anything.